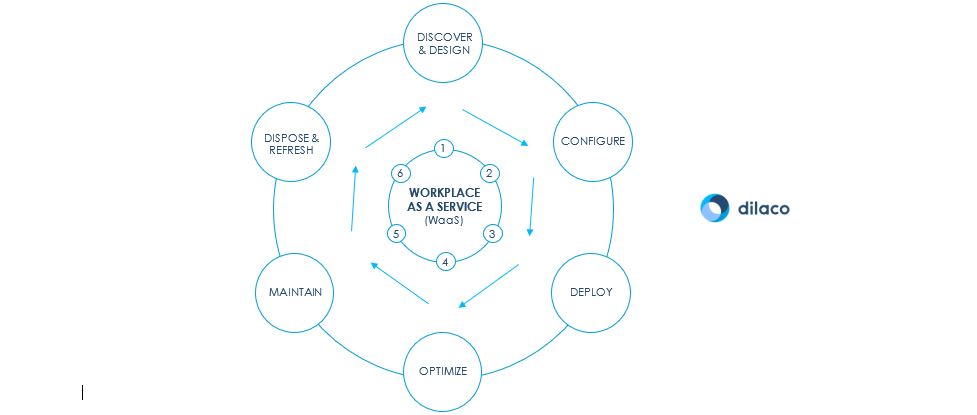
The six steps of WaaS
1. Design workshop
The experts meet with the different stakeholders in the organisation to work out all the requirements on the work floor for IT tooling. They also discuss the different environments where people work (in the office, at home, on the way, etc.).
The outcome of such a design workshop is a clear plan of what we are going to be configuring, deploying and supporting.
2. Configuration
The next step is configuration. Configuration means putting the software and hardware together and preparing for deployment. It is here that project management starts to be very important.
3. Deployment
Deployment is bringing all the equipment to the right places, distributing it, installing it and making sure that it works flawlessly for everybody.
This can be done by actual physical distribution, bringing it to the workplace and installing it. But the equipment can also be deployed by using smart lockers and putting the equipment in those lockers, so that employees can pick it up whenever they are able to.
4. Optimization
Once everything is installed and up and running, we proceed to the optimization phase. This is mostly done by a helpdesk and the different support levels.
First line experts are technical experts resolving most of the problems that come their way. There can be a differentiation in services, depending on how your organisation operates. With for example VIP services for more prominent users and/or standard services for most other users. The first line support officers are supported by second line experts, who in turn are supported by third line experts.
5. Maintenance
Maintenance is not just sorting out issues. Actually, maintenance is mainly aimed at preventing issues from occurring. Making sure that all the equipment is always running and permanently monitored. It also means proactively reacting whenever the data shows that a problem might occur. Obviously, in some cases problems might still occur and than it is a matter of resolving the issues in the quickest possible way, with the most efficient approach.
6. Disposal & Refreshment
After a number of years, the IT equipment will be depreciated and the technology will be outdated. So then we move to the disposal and refreshment phase.
Refreshment, because you want to make sure that all the users have access to the newest and best technology in order to be productive and efficient in their work.
Disposal is not just taking back all the equipment and getting rid of it. The best practice here is sustainable asset management. What does this mean? It means using advanced processes and technology to take apart the old equipment to the lowest possible level in order to be able to put the materials back into the industrial supply chain. As such, we enable the circular economy and protect our natural habitat.
We hope that this article has shed some light on what Workplace-as-a-Service actually consists of. If you have any questions, please reach out. We will be more than happy to help you!